
What is Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-Factor Authentication, also known as 2FA, two-step verification, or dual-factor authentication is an added level of security when logging in that requires you to confirm your identity through two authentication factors.
Two-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to the sign-in processes for websites and apps by making it harder for hackers to gain access to a person’s devices or online accounts. Even if the person’s password is stolen, 2FA can help keep the data safe because unlike single-factor authentication, 2-factor authentication relies on both a password and usually either a security token or a biometric factor, like a code sent to a mobile number or a fingerprint/facial scan to sign in.
Now that you know what 2-factor authentication is, it’s equally important to understand why 2FA is necessary and why using a password alone isn’t enough.

Why Isn’t a Password Enough?
With hackers and cybercriminals developing new ways of stealing information, it is now more important than ever to make sure your data is secure. Single-factor authentication methods like entering a password are now proving to not be enough. Hackers can use methods like phishing campaigns to steal your information (phishing campaigns are when a hacker poses as a reputable company or person to try and steal your information via email by asking you to click on a link, enter your information, etc.), in order to gain access to important data like bank passwords, addresses, and more. Simply put, only using a password or even a pin to protect your data will not be enough to stop a hacker.
Along with providing poor protection against hackers, single-factor authentication methods fall victim to user error as well. User error when making a password normally falls under these reasons:
- Your passwords are too simple. It was shown in a recent report that out of 1.4 billion passwords stolen, almost all of them were too simple. Users were reported to be using passwords like “111111,” “123456,” “123456789,” “qwerty,” and “password.” Even though these passwords are easy to remember, any hacker could figure these out with no problem. A good rule to remember when making a password is to pick something that no one else would know, and something that isn’t easily guessed (so, don’t use passwords like “123456”).
- You have too many accounts open. When you open more and more accounts online, password recycling becomes more and more of a threat. Password recycling is when you reuse a password from one account for another, making it even easier for hackers to get into your information. These hackers can use software in order to test thousands of stolen sign-in credentials for popular online banks and shopping sites, and if you’re prone to reusing passwords, a hacker will have an even easier time figuring out your credentials. To avoid the problem of password recycling, you should keep track of all accounts you have open and when you created them, even if you just signed up to use a one-time coupon at Target. Even though this can help prevent the reuse of passwords, it is recommended you still enable a two-factor sign-in method.
By now you have probably figured out that two-factor authentication is safer than just using a single-factor sign-on, but what is a factor of authentication?

The Two-Factor Basics
There are a few different ways two-factor authorization can work. However, almost all two-factor processes first require a username and password, and then instead of immediately gaining access, you will be asked to provide a second authentication factor. That second factor normally falls under one of these categories:
- Something you know: a password, a question (e.g., what’s your childhood pet), or any other “secret” information.
- Something you own: a smartphone, credit card, or anything else you have that can prove your identity.
- Something you possess: a fingerprint, a face ID or scan, or any other method of verification such as a voice authentication.
Software Token
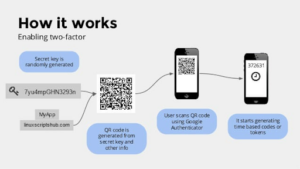
That second factor of authentication could also be a one-time code/pin (OTP) sent to your cell number or email and entered on the website, a push notification sent to a device like your cellphone, a hardware token (a small, key-fob-sized unit that produces a new numerical code every 30 seconds, and are normally used at businesses) or a software token, which is a one-time passcode or “soft-token” (TOTP) generated by time-based software, which you access through an app.
How It Works
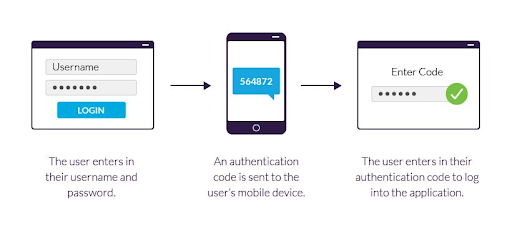
Setting up and using two-factor authentication typically follows the same process:
- You will be asked to log in or sign up with your username and password on the app/website you’re on.
- A second method of verification will be requested, whether it be a pin sent to your cell or providing a fingerprint. If you’re setting up an account using 2FA, you may be asked to provide your phone number, email, and proof of ID or answer a security question to set up that second verification form.
What next?
Now that you know the importance of enabling two-factor authentication when signing in to any account, you may wonder how you set it up or figure out if it is already on. That’s where our IT technicians can help! As part of our regular maintenance visits, our technicians will ensure you have two-factor set up and turned on for all your accounts and will help you set up 2FA if you don’t already have it. To make an appointment with one of our technicians, call us at 732-681-2360.



